What Is an Ethernet Cable: The Ultimate Guide to Wired Network Connectivity in 2025
When someone asks what an Ethernet cable is, they're really asking about one of the most reliable ways to connect devices to the internet and local networks. While WiFi gets all the attention these days, ethernet cables quietly power the backbone of our digital world—from your home office setup to massive data centers running your favorite apps.
Think of Ethernet cables as the highways of the internet. They carry data at lightning speed without the traffic jams and interference that wireless connections often face. Let's explore everything you need to know about these essential networking tools.
What Is an Ethernet Cable: The Basics Explained
An Ethernet cable is a physical wire that connects your devices to networks using the IEEE 802.3 standard. These cables create a direct, dedicated path for data between computers, routers, switches, and other network equipment. Unlike WiFi signals that bounce around and can get blocked by walls or interfered with by other devices, Ethernet cables provide a straight shot for your data.
How Ethernet Got Started: A Quick History Lesson
Back in 1973, Bob Metcalfe created Ethernet technology at Xerox PARC. By 1983, the IEEE made it an official standard (IEEE 802.3). The early days involved thick, clunky coaxial cables that were a pain to install. Over time, these evolved into the much more manageable twisted-pair cables we use today, plus fiber optic options for super-high-speed connections.
Clearing Up the Name Game: Ethernet vs Network vs LAN Cables
People often mix up these terms, but here's the deal:
- Ethernet Cable: Follows specific IEEE 802.3 rules and standards
- Network Cable: Catch-all term for any cable used in networking
- LAN Cable: Usually refers to cables used in local networks (most commonly Ethernet).
Most of the time, when people say any of these terms, they're talking about the same thing—standard Ethernet cables.

How These Cables Actually Work
The Magic Behind Data Transmission
Ethernet cables follow the IEEE 802.3 standard, which sets the rules for how fast data can travel and how it gets packaged for the journey. Data moves as electrical signals through copper wires or as light pulses through fiber optic cables. The system includes built-in error checking to make sure your data arrives intact.
Why Twisted Pairs Make All the Difference
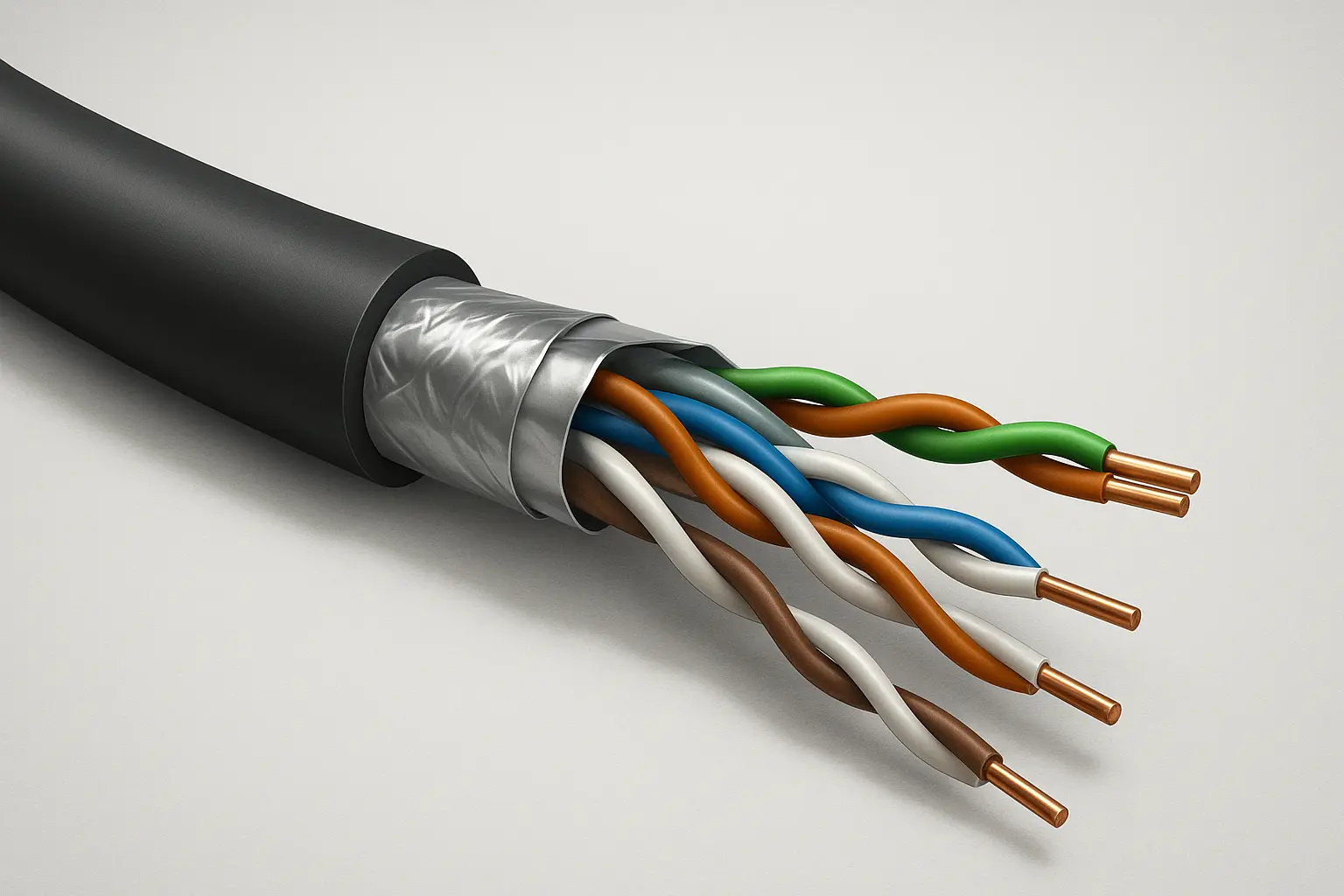
Most Ethernet cables use something called twisted pair technology. Inside the cable, you'll find eight copper wires arranged in four pairs, with each pair twisted together. This isn't just for looks—the twisting cancels out interference from electrical noise and prevents the wire pairs from messing with each other's signals. Pretty clever engineering that lets these cables work reliably over distances up to 100 meters.
What's Inside an Ethernet Cable
The Core Components
Modern Ethernet cables have several layers:
- Conductors: Eight copper wires that carry the actual signals
- Insulation: Coating around each wire to prevent electrical shorts
- Jacket: Tough outer covering that protects everything inside
- Shielding: Optional metal barriers that block interference
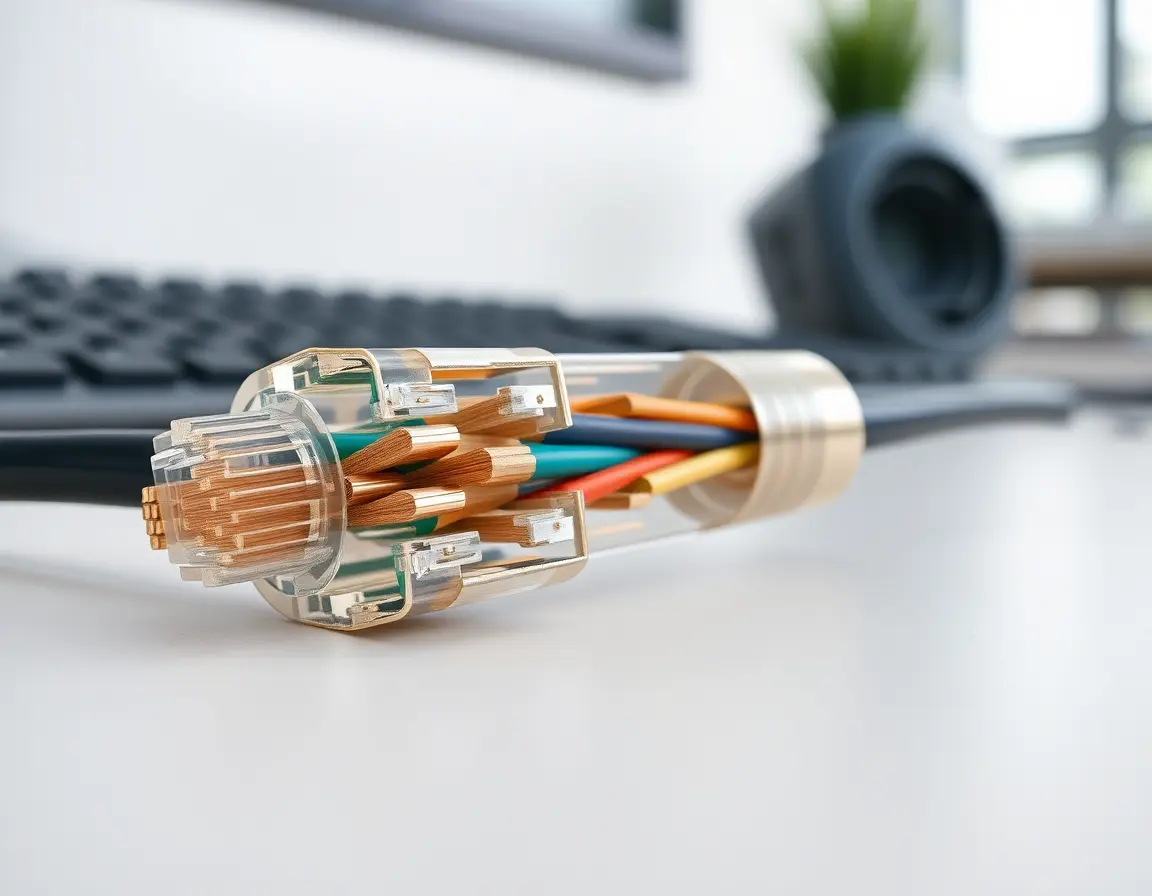

Solid vs. Stranded Wire: Which Is Better?
Solid-core cables use single thick copper conductors. These work great for permanent installations like running cables through walls because they maintain signal quality over long distances better.
Stranded-core cables use multiple thin wires bundled together for each conductor. They're more flexible, making them perfect for patch cables that get moved around frequently. The trade-off is slightly reduced performance over very long runs.
Choosing the Right Jacket Material
The outer jacket protects your cable from the environment:
- PVC: Standard choice for most indoor setups
- LSZH (Low Smoke Zero Halogen): Safer option for enclosed spaces since it doesn't release toxic fumes if it burns
- Polyurethane: Tough option for industrial settings where cables get beat up
- Outdoor-rated: Weather-resistant materials for external installations
Ethernet Cable Categories: Understanding Speed and Performance
Cable categories determine how fast your network can run and how far signals can travel reliably.
Cat5e: The Reliable Workhorse
Category 5e cables handle frequencies up to 100 MHz and support gigabit speeds (1 Gbps) over 100 meters. They're the minimum you should consider for new installations today. Cat5e offers great value for home networks and small businesses that don't need extreme speeds.
Cat6: Stepping Up Performance
Category 6 cables bump up the frequency to 250 MHz. They'll do gigabit speeds over the full 100-meter distance and can handle 10 gigabit speeds over shorter runs (usually around 55 meters). The improved construction reduces crosstalk between wire pairs.
Cat6a: Full 10 Gigabit Support
Category 6a extends that 10-gigabit performance to the full 100-meter distance with 500 MHz bandwidth. These cables cost more but future-proof your installation better. They're becoming the go-to choice for businesses planning to upgrade their networks.
Cat7 and Cat8: The Speed Demons
Category 7 cables provide 600 MHz bandwidth with heavy-duty shielding, while Category 8 cables push bandwidth to 2000 MHz and support speeds up to 40 Gbps over 30 meters. These serve specialized needs in data centers and high-performance computing environments.
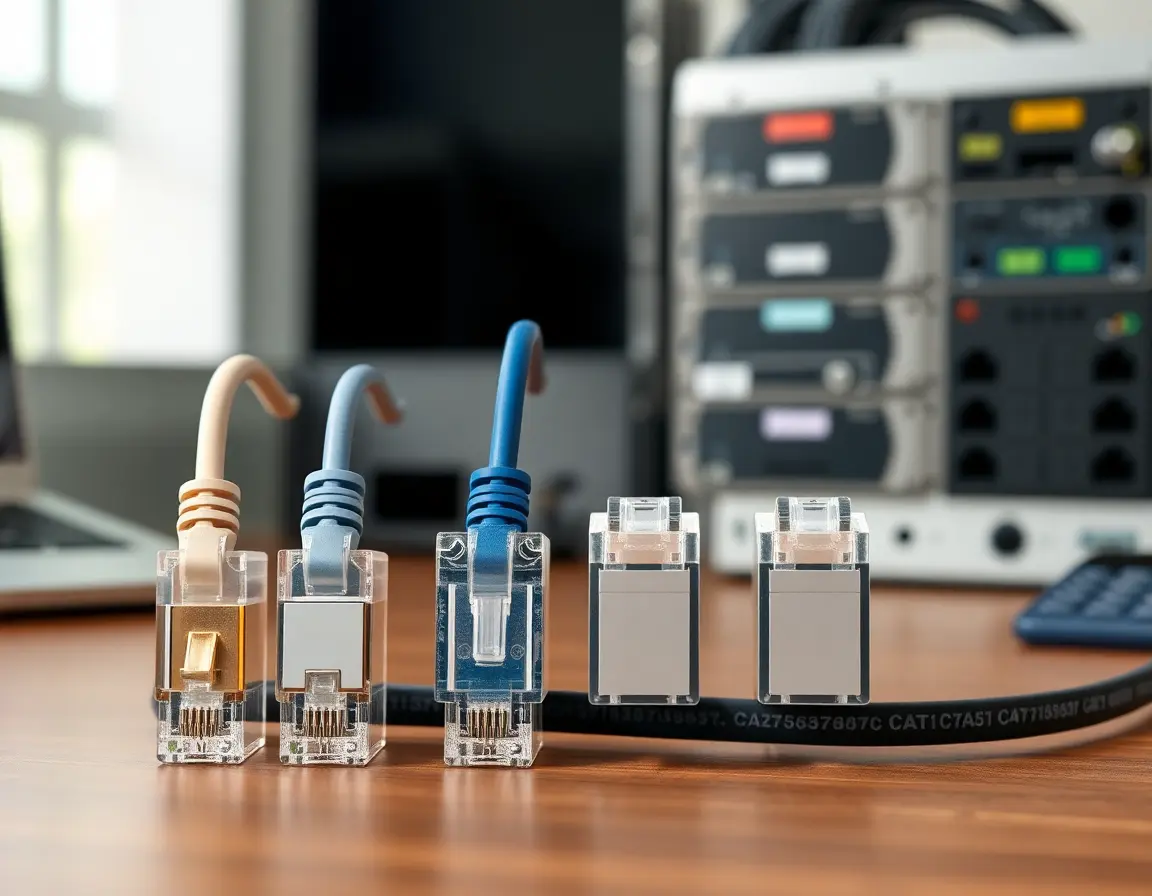

Understanding Cable Shielding Options
Basic Shielding Types
Shielding helps block electromagnetic interference:
- UTP (Unshielded Twisted Pair): No extra shielding—relies on the twisted pairs alone
- FTP (Foil Twisted Pair): Thin foil wrapper around all the wire pairs
- STP (Shielded Twisted Pair): Metal braid shield around individual pairs plus overall shielding
Heavy-Duty Protection: S/FTP and S/STP
S/FTP combines foil shields around each wire pair with an overall braided shield. S/STP goes even further with braided shields on individual pairs and overall construction. These provide maximum protection in electrically noisy environments like factories or near heavy machinery.
Connectors and Wiring: Getting Connected Right
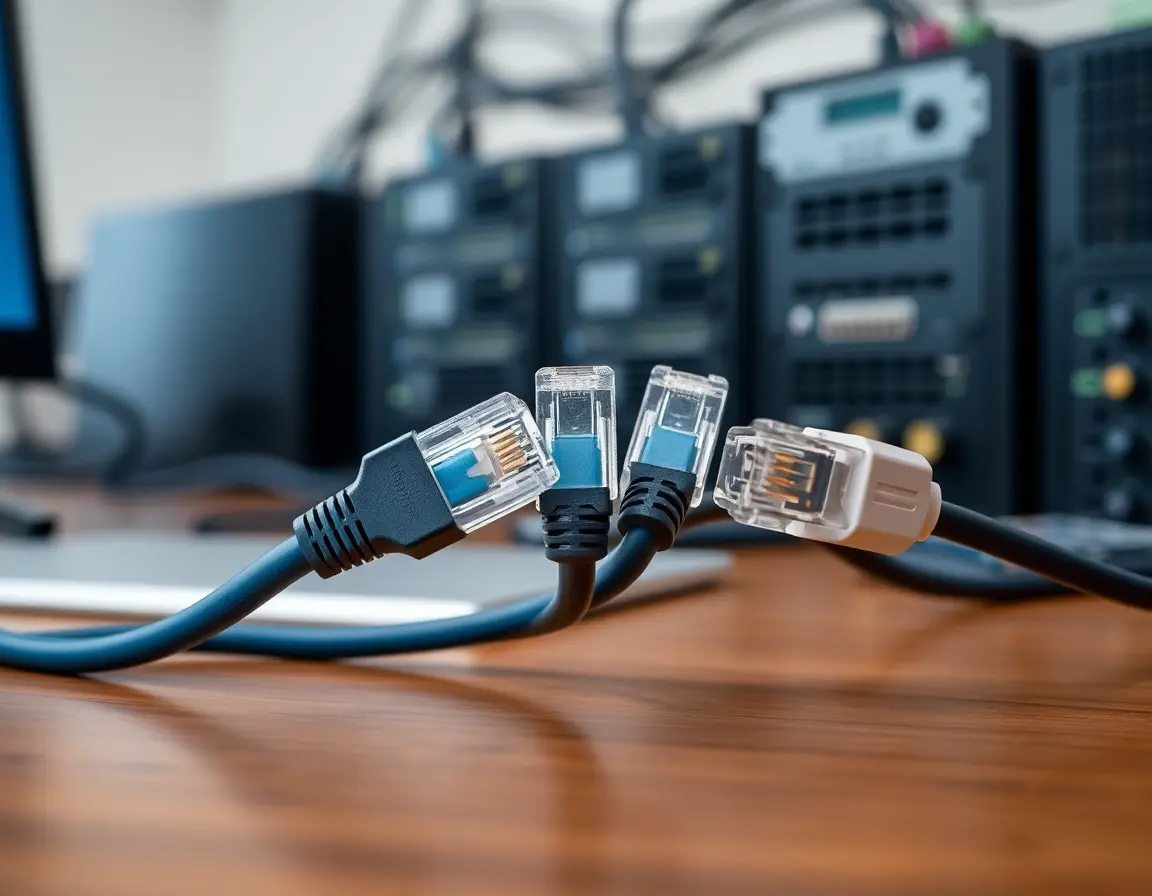
RJ45: The Standard Connection
Almost all Ethernet cables use RJ45 connectors (technically called 8P8C). These plastic connectors have eight pins that match up with the eight wires in the cable. Proper crimping is essential for reliable connections.
Wiring Standards: T-568A vs T-568B
Two main wiring standards exist:
- T-568B: More popular in commercial installations
- T-568A: Alternative standard that works just as well
Pick one and stick with it throughout your installation. Most people go with T-568B since it's more common.
Straight-Through vs. Crossover: What's the Difference?
Straight-through cables connect different types of devices (like a computer to a switch). Crossover cables used to be needed to connect similar devices directly to each other. Modern equipment usually handles this automatically with Auto-MDIX technology, so you can stick with straight-through cables for almost everything.
Where Ethernet Cables Shine
Home and Small Office Setup
Ethernet cables provide rock-solid connections for desktop computers, gaming systems, smart TVs, and network storage devices. Gamers especially love wired connections because they eliminate the lag and packet loss that can happen with WiFi.
Business Networks
Companies rely on Ethernet cables to connect switches, routers, and servers. These backbone connections form the foundation of office communication systems and need to be extremely reliable.
Industrial and Manufacturing
Factories use specialized Ethernet cables that can handle vibration, temperature extremes, and electrical interference. These networks control manufacturing equipment and safety systems where reliability is life-or-death important.
Data Centers: Where Speed Matters Most
High-performance Ethernet cables (Cat6a and above) connect servers, switches, and storage systems in data centers. Every millisecond counts when you're serving millions of users.

Power over Ethernet: Two Services, One Cable
What PoE Can Do
Power over Ethernet sends both data and electricity through a single cable. This technology powers devices like security cameras, wireless access points, and office phones without needing separate power outlets.
PoE comes in different flavors:
- Standard PoE: Delivers 15.4 watts
- PoE+: Bumps up to 25.5 watts
- PoE++: Goes up to 100 watts for power-hungry devices
Cable Requirements for PoE
PoE needs quality cables with proper wire gauge (usually 23 or 24 AWG) to handle power safely. Higher-power PoE works better with Cat6 or better cables since they have less voltage drop and generate less heat.
Picking the Right Cable for Your Needs
Matching Speed Requirements
Choose cables based on your network speeds:
- Up to 1 gigabit: Cat5e works, but Cat6 is better for the future
- Up to 10 gigabits: Cat6a for full distance, Cat6 for shorter runs
- 25+ gigabit: Cat8 for data center connections
Environmental Considerations
Your installation environment affects cable choice:
- Standard indoor: UTP cables with PVC jackets work fine
- Electrically noisy areas: Go with shielded cables (FTP, STP, or S/FTP)
- Fire-sensitive buildings: Use LSZH jacket materials
- Outdoor runs: Get UV-resistant, waterproof cables
Installation Tips That Actually Matter
Handle With Care
Keep cable bends gentle—maintain at least four times the cable diameter as your minimum bend radius. Don't yank on cables during installation, and avoid sharp edges that can damage the jacket.
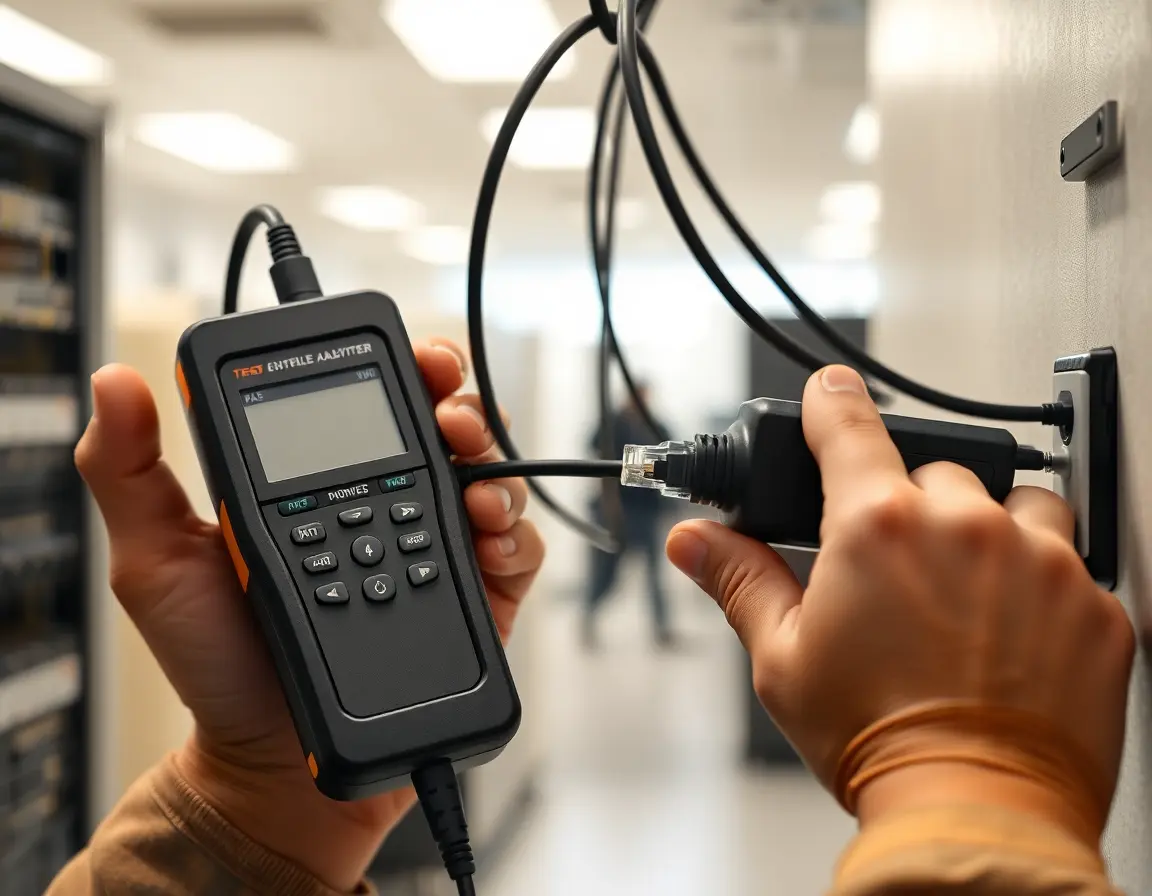
Test Before You Trust
Professional installations should always include testing with cable analyzers to check:
- Continuity: All wires connected properly
- Wire mapping: Pins connected to the right places
- Performance: Signal quality meets specifications

Planning for the Future
What's Coming Next
Ethernet keeps getting faster with new standards like 25GBASE-T and 40GBASE-T for copper cables. Installing higher-category cables than you currently need helps avoid costly rewiring later.
When Fiber Makes Sense
Copper ethernet cables work great for most situations, but fiber optic cables become necessary when you need:
- Longer distances(over 100 meters)
- Extreme speed requirements
- Total immunity to electrical interference
- Electrical isolationbetween buildings
Why Ethernet Cables Still Matter
Understanding what is an ethernet cable and choosing the right one makes a real difference in network performance. Whether you're setting up a home office or designing a corporate network, the right cable selection and proper installation create a solid foundation for reliable communications.
Ethernet technology keeps evolving to meet growing demands while staying compatible with existing equipment. This balance of performance, reliability, and cost-effectiveness explains why ethernet cables remain the gold standard for wired networking.
Good cables properly installed will serve you well for years. Take time to plan your installation, choose appropriate cable categories, and test everything properly. Your future self will thank you when your network just works, day after day, without the headaches that come with poor cable choices.










